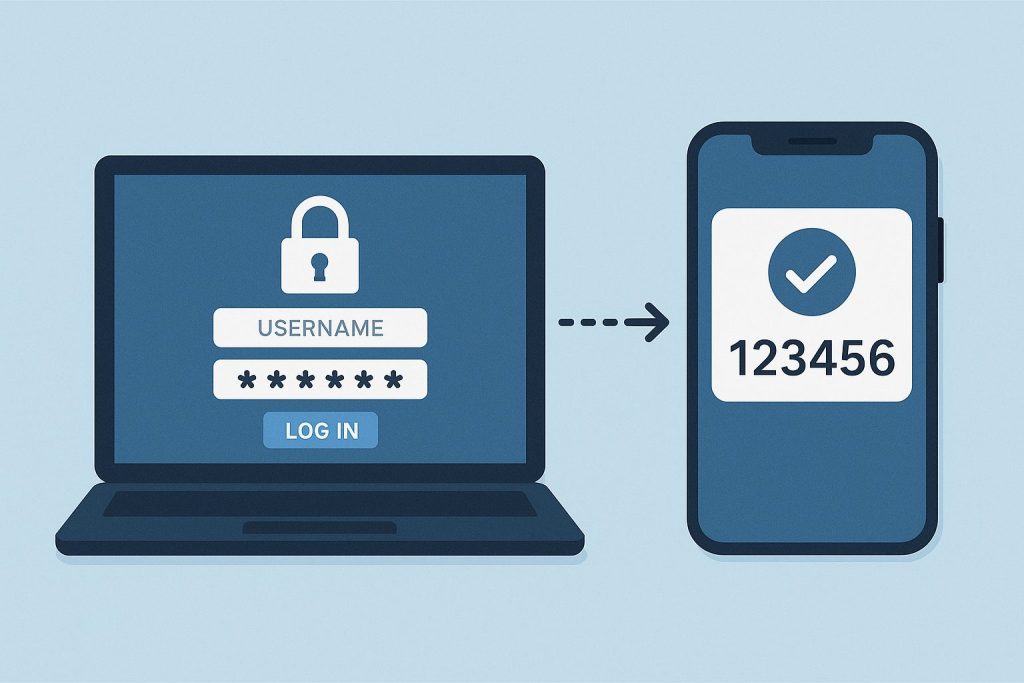
In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats loom large and data breaches are increasingly common, safeguarding sensitive information is paramount. One of the most effective methods of fortifying online security is through the implementation of two-factor authentication (2FA). This additional layer of protection offers a robust defense against unauthorized access, significantly reducing the risk of identity theft, data breaches, and financial losses. Understanding the mechanics of 2FA and the vulnerabilities it addresses is crucial in appreciating its importance in safeguarding personal and organizational assets.
Understanding Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication is a security process that requires users to provide two different authentication factors to verify their identity. These factors typically fall into three categories:
- Knowledge Factors: Something only the user knows, such as a password or a PIN.
- Possession Factors: Something only the user has, such as a smartphone, token, or smart card.
- Inherence Factors: Something inherent to the user, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
The most common implementation of 2FA involves combining a password (knowledge factor) with a unique, time-sensitive code sent to a trusted device (possession factor), such as a mobile phone. Upon entering their password, users must then input the verification code to gain access to their account or system.
The Vulnerabilities of Passwords
Passwords, despite being the most widely used form of authentication, are inherently vulnerable to exploitation. The rise of sophisticated hacking techniques and the prevalence of data breaches have rendered traditional password-based authentication inadequate. Hackers employ various methods to compromise passwords, including:
- Brute Force Attacks: Hackers use automated tools to systematically guess passwords until they find the correct one. With sufficient computing power, even complex passwords can be cracked relatively quickly.
- Phishing: Cybercriminals trick users into divulging their passwords by posing as legitimate entities through deceptive emails, websites, or messages.
- Keylogging: Malicious software secretly records keystrokes, enabling attackers to capture passwords as users type them.
- Dictionary Attacks: Hackers use predefined lists of commonly used passwords or words from dictionaries to crack passwords more efficiently.
The Implications of Password Vulnerabilities
The consequences of password vulnerabilities can be severe, ranging from compromised personal accounts to large-scale data breaches with far-reaching implications. Once hackers gain access to an individual’s account, they can:
- Steal Sensitive Information: Access to personal emails, financial accounts, or confidential documents can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, or corporate espionage.
- Impersonate Users: Hackers can masquerade as legitimate users to perpetrate further cybercrimes, such as spreading malware or launching phishing attacks.
- Cause Reputational Damage: Data breaches resulting from compromised passwords can tarnish an individual’s or organization’s reputation, leading to loss of trust among customers, partners, and stakeholders.
The Role of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication addresses many of the vulnerabilities associated with password-based authentication by adding an extra layer of security. Even if hackers manage to obtain a user’s password through illicit means, they would still require access to the second factor (e.g., a mobile device) to successfully authenticate. This significantly reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access, as it becomes exponentially more challenging for attackers to compromise both factors simultaneously.
Conclusion
In an era marked by escalating cyber threats and increasingly sophisticated hacking techniques, the importance of two-factor authentication cannot be overstated. By augmenting traditional password-based authentication with an additional layer of security, 2FA offers a potent defense against unauthorized access and data breaches. Embracing 2FA not only enhances individual and organizational security but also instills confidence in users that their sensitive information remains protected in an ever-evolving threat landscape. As we navigate the digital realm, prioritizing robust security measures like two-factor authentication is essential to safeguarding our digital identities and preserving trust in the online ecosystem.
Leave a Reply